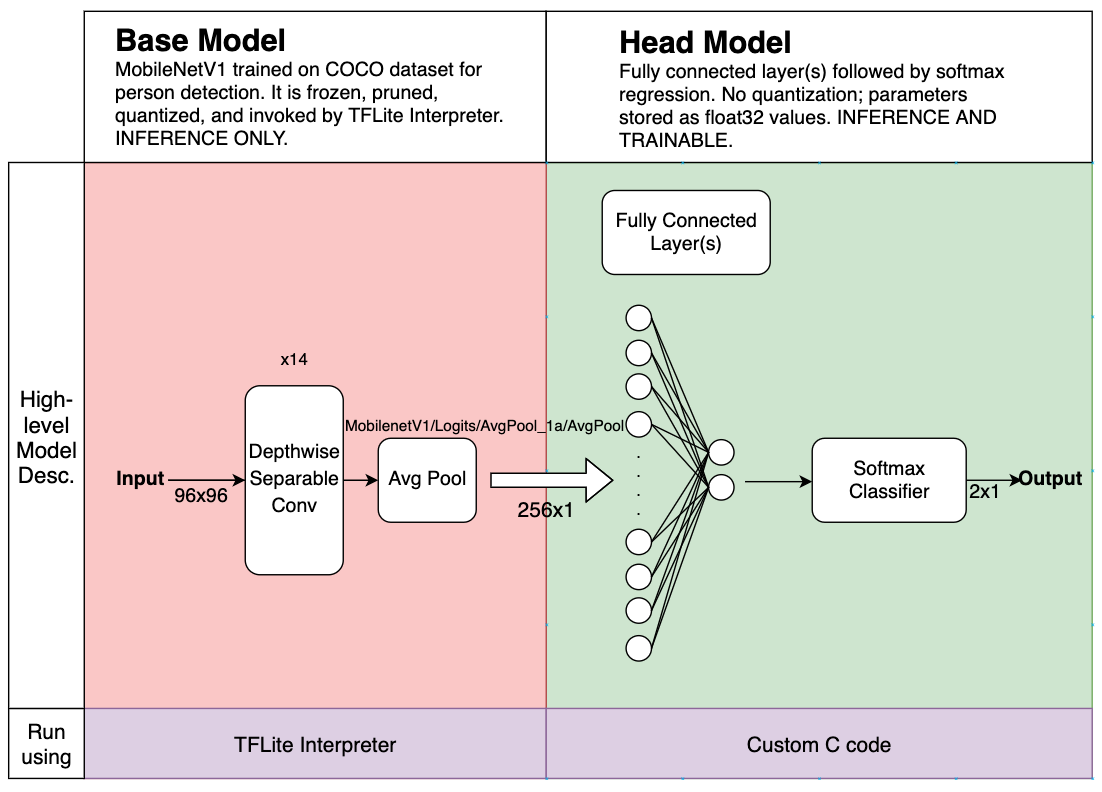
Methods in Extending RL to LQR Adaptive Control: A Survey
Published:
Learning-theoretic work on extending fundamental RL algorithms to LQR Adaptive Control has recently (over the last decade) received more attention. Inspired by the significant progress made independently in RL and adaptive control, this fusion of approaches shows significant promise with potential applications in robotics, plant operations, and game theory (to name a few). This survey is intended to provide the reader with an overview of the recent algorithms and significant theoretical results obtained in extending RL to LQR Adaptive control. This study is done with regards to the benchmark discrete-time, infinite-horizon LQR with unknown dynamics. Regret analyses are presented, and detailed discussions that compare and contrast the methods are provided.